Welcome to my website!
Applied AI/ML · Probabilistic Modeling · Data Science · Computer Simulations · High Performance Computing
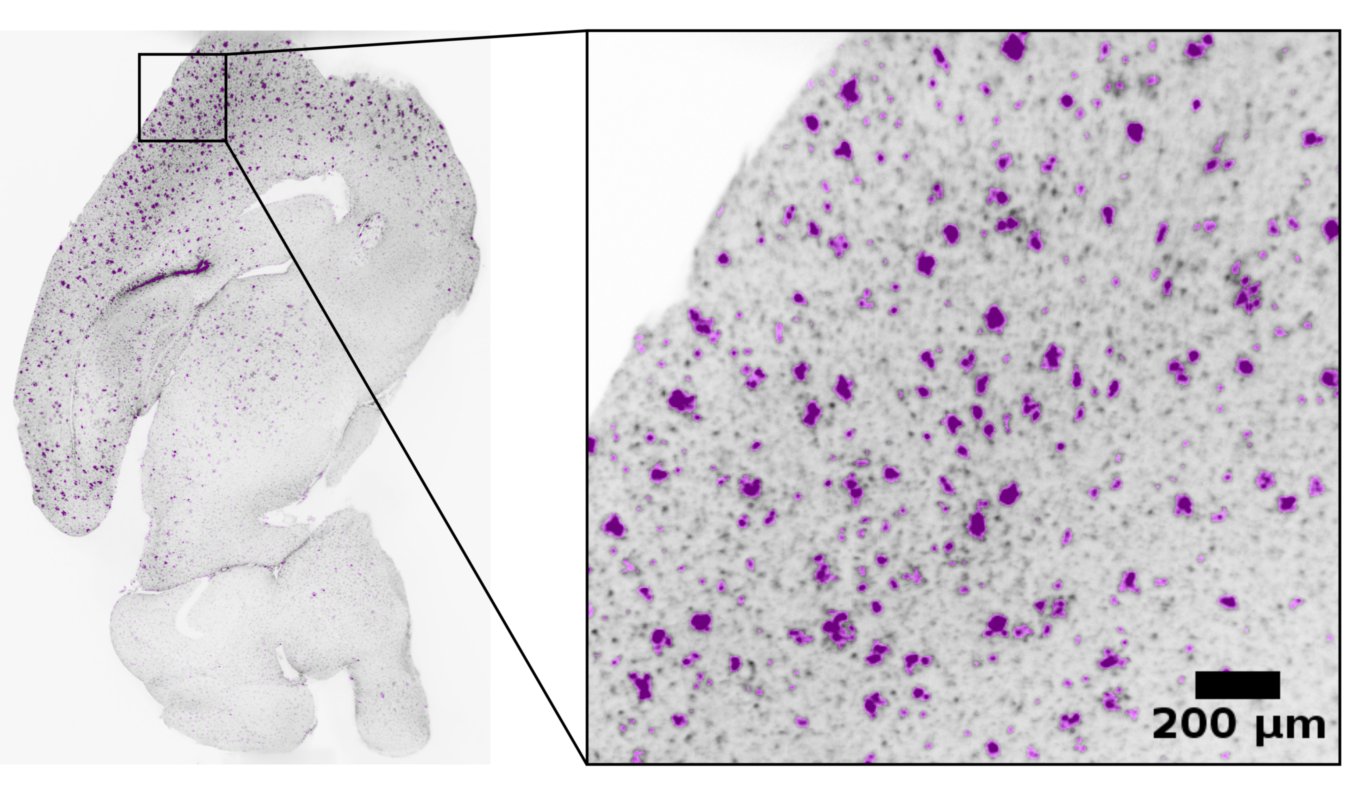
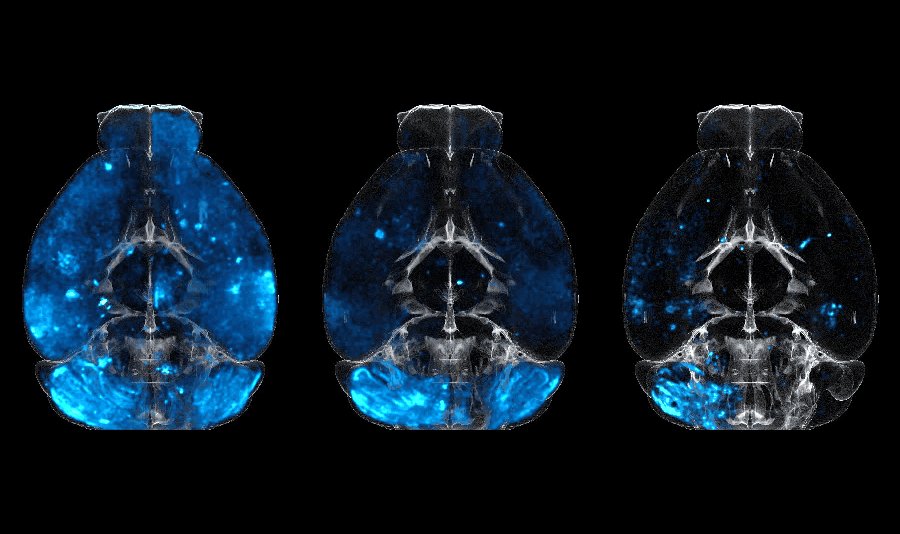
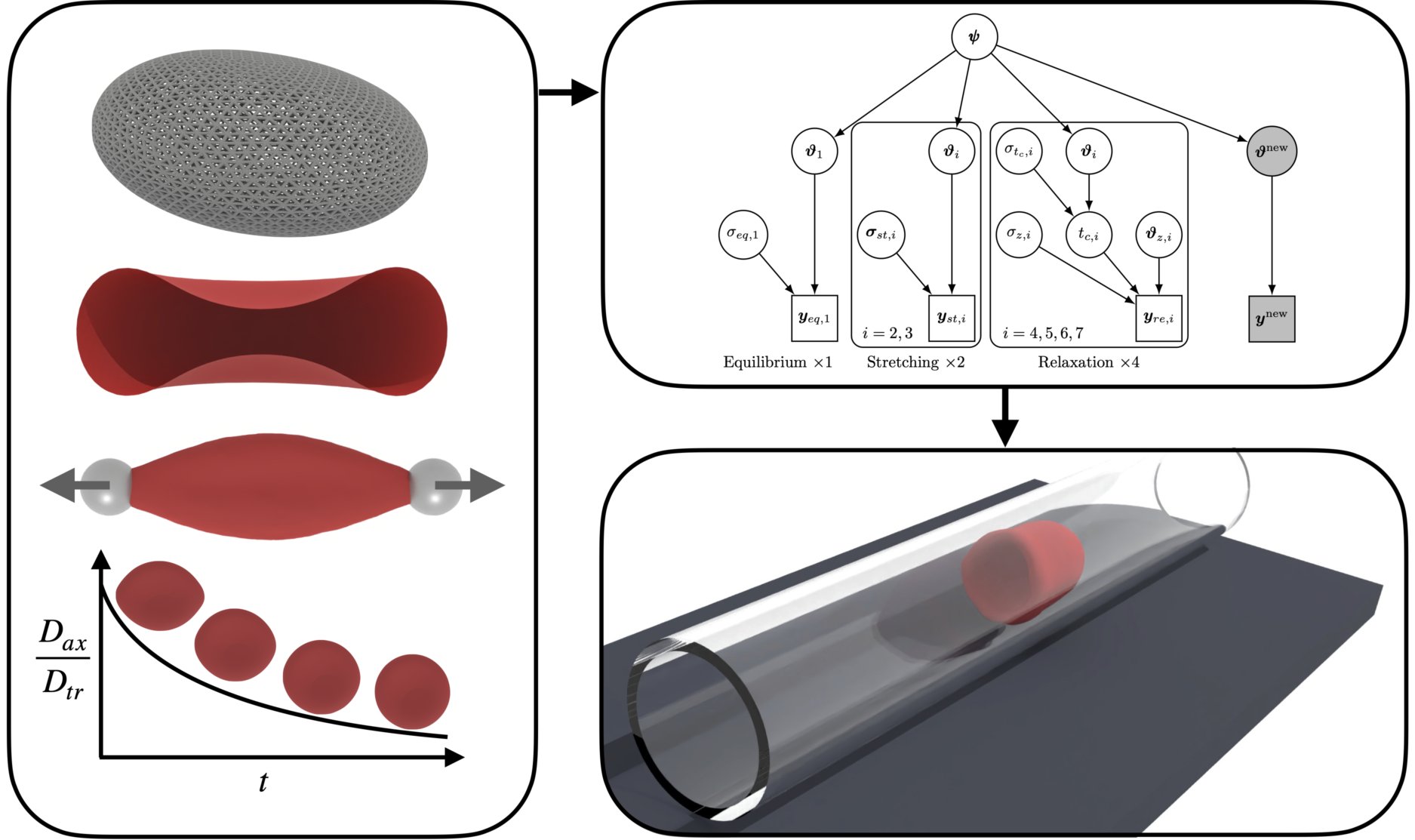
A few highlights are showcased below — you can explore the full set on the Projects page.
Selected Research Projects
Open-Source Software